Feta Cheese and Dietary Considerations
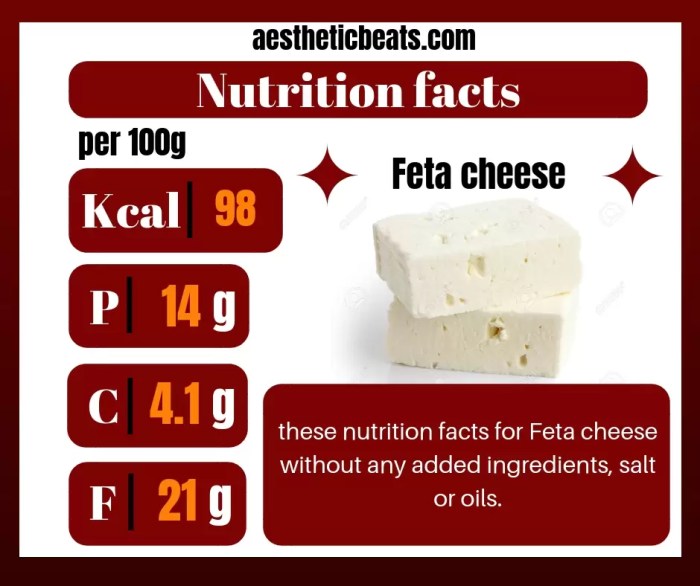
Feta cheese nutrition label – Feta, a salty, tangy delight, holds a unique place in the culinary world. Its nutritional profile, however, deserves careful consideration within the context of various dietary approaches. Understanding its composition allows us to integrate it mindfully into a healthy lifestyle, aligning our food choices with our overall well-being. This exploration will illuminate feta’s role in different diets and offer a balanced perspective on its potential benefits and drawbacks.
Feta cheese, with its distinctive flavor and creamy texture, presents a fascinating study in nutritional balance. It offers a source of protein and calcium, vital for building and maintaining strong bones and muscles. Yet, like all foods, moderation and awareness are key to its responsible consumption. Let us delve into its suitability across different dietary patterns.
Understanding a feta cheese nutrition label is key to mindful eating. For a comparison, you might find it interesting to check out the brie cheese nutrition facts , as both cheeses offer different nutritional profiles. Returning to feta, remember to consider serving size when reviewing its fat and sodium content for a balanced diet.
Feta Cheese and Low-Carb/Ketogenic Diets
Feta cheese can be a valuable addition to low-carbohydrate and ketogenic diets due to its relatively low carbohydrate content. A serving of feta provides a satisfying amount of fat and protein, contributing to satiety and helping to maintain ketosis. However, it’s crucial to monitor portion sizes as even low-carb options can accumulate calories and affect overall macronutrient balance.
Consider incorporating feta into salads, keto-friendly baked goods, or as a topping for vegetables. Always check the nutritional information on the specific brand of feta you are using, as carbohydrate content can vary slightly.
Feta Cheese and the Mediterranean Diet
Feta cheese is a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, a dietary pattern celebrated for its potential health benefits. Its inclusion reflects the diet’s emphasis on healthy fats, dairy products, and fresh produce. In the context of the Mediterranean diet, feta complements a vibrant array of vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, creating a balanced and flavorful meal plan. The moderate consumption of feta within this framework contributes to a holistic and nourishing approach to eating.
Comparison of Feta Cheese with Other Cheeses
Understanding the nutritional differences between various cheeses is crucial for making informed choices. Comparing feta to popular cheeses like mozzarella and cheddar reveals interesting distinctions.
- Fat Content: Feta generally has a higher fat content than mozzarella, but a lower fat content than cheddar. This difference stems from the manufacturing process and the type of milk used.
- Sodium Content: Feta cheese is typically higher in sodium than both mozzarella and cheddar, a factor to consider for individuals monitoring their sodium intake.
- Protein Content: All three cheeses provide a good source of protein, though the exact amount varies slightly depending on the brand and type of milk used.
- Calcium Content: Feta, mozzarella, and cheddar all offer a significant amount of calcium, contributing to bone health.
Health Benefits and Risks of Feta Cheese Consumption
Regular consumption of feta cheese, like any food, presents both potential benefits and risks. Moderation is key to maximizing benefits and minimizing potential drawbacks.
- Potential Benefits: Feta provides calcium and protein, contributing to bone health and muscle building. It also contains beneficial fatty acids.
- Potential Risks: High sodium content can be a concern for individuals with hypertension. Excessive consumption of saturated fat can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels. Those with lactose intolerance should consume feta in moderation or opt for lactose-free alternatives.
Visual Representation of Feta Cheese Nutrition: Feta Cheese Nutrition Label

Understanding the nutritional content of feta cheese is a journey of self-discovery, a path towards mindful eating. By visualizing the information presented on a nutrition label, we unlock the power to make conscious choices that nourish our bodies and souls. This visual approach transforms numbers into a tangible understanding of what we consume.
A typical feta cheese nutrition label, much like a spiritual map, guides us through the landscape of its nutritional composition. Imagine a rectangular box, divided into sections. At the top, prominently displayed, is the brand name and the weight of the serving size, usually in grams and ounces. Below, a clear, concise list details the macronutrients: Total Calories, Total Fat, Saturated Fat, Trans Fat, Cholesterol, Sodium, Total Carbohydrate, Dietary Fiber, Total Sugars, and Protein.
Each nutrient’s quantity is presented in grams, milligrams, or as a percentage of the recommended daily intake (%DV). This percentage is crucial for understanding how a serving fits into our overall daily dietary needs. The label also lists Vitamins and Minerals, such as Calcium and Vitamin A, often represented as %DV. The visual clarity of this arrangement simplifies the process of understanding the nutritional profile of feta cheese.
Feta Cheese Nutritional Content Compared to Other Dairy Products
A comparative visual representation can further illuminate the nutritional landscape. Imagine a bar graph, with each bar representing a different dairy product: feta cheese, cheddar cheese, milk, yogurt. The height of each bar corresponds to the amount of a specific nutrient, such as fat or protein. For instance, the bar representing feta cheese might be taller in the “fat” section than the “protein” section, reflecting its higher fat content compared to yogurt.
Similarly, the cheddar cheese bar might be taller than the feta cheese bar in the saturated fat category, offering a visual comparison of their saturated fat profiles. This visual comparison empowers us to make informed choices based on our individual dietary goals and preferences, aligning our consumption with our inner wisdom.
Interpreting Feta Cheese Nutrition Labels for Informed Dietary Choices
Interpreting a nutrition label is not merely deciphering numbers; it’s about understanding the impact of our choices on our well-being. Consider a feta cheese label indicating a high sodium content. This information guides us towards mindful consumption, prompting us to balance our sodium intake throughout the day. If we’re watching our fat intake, we can compare the fat content of feta to other cheeses or dairy alternatives, making choices that align with our health goals.
The percentage of daily value (%DV) for each nutrient serves as a compass, guiding us toward a balanced and nourishing diet. For example, a high %DV for calcium highlights feta’s contribution to bone health. By engaging with this information, we become conscious participants in our own well-being, fostering a relationship with food that is both nourishing and spiritually fulfilling.
The label becomes a tool for self-awareness, a guide on our journey towards a healthier and more harmonious life.
FAQ Overview
Is feta cheese high in sodium?
Yes, feta cheese is relatively high in sodium due to the salting process. Be mindful of your intake if you’re watching your sodium levels.
Can I eat feta cheese if I’m lactose intolerant?
It depends on your level of lactose intolerance. Feta cheese is aged, which reduces lactose content, but some people still experience issues. A small amount might be tolerable, but it’s best to listen to your body.
How long does feta cheese last?
Properly stored feta cheese can last for several weeks in the refrigerator. Look for signs of mold or spoilage before consuming.
Is feta cheese good for weight loss?
Feta cheese can be part of a healthy weight loss diet in moderation. It’s a good source of protein, but it’s also relatively high in fat and calories, so portion control is essential.
