Nutritional Composition of Cheese Sticks
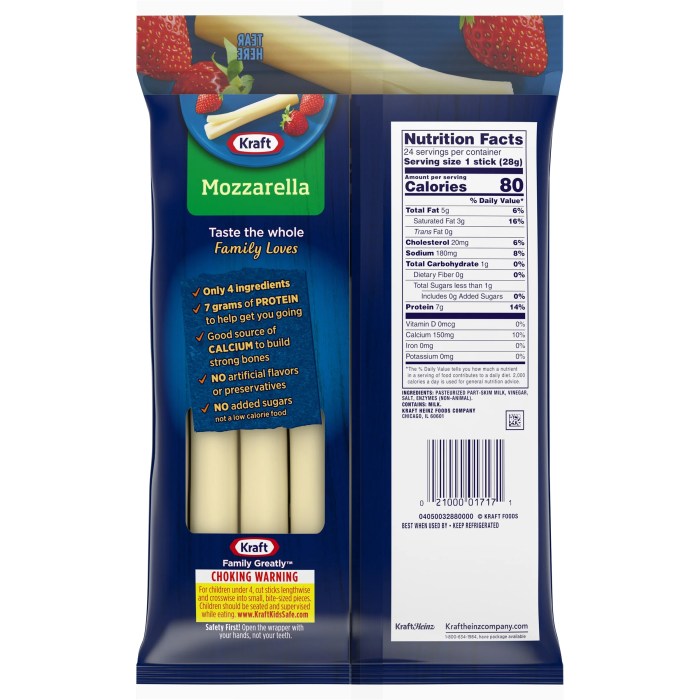

Cheese stick nutrition information – Cheese sticks, a convenient and popular snack, offer a readily available source of protein, fat, and calcium. However, their nutritional profile varies considerably depending on the type of cheese used and the manufacturing process. Understanding this variation is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
Macronutrient Composition of Cheese Sticks
A typical one-ounce (approximately 28-gram) cheese stick provides a significant amount of protein and fat, with a relatively low carbohydrate content. The exact proportions vary depending on the cheese type and brand, but generally, a cheese stick will contain between 6-8 grams of protein, 7-10 grams of fat, and 1-2 grams of carbohydrates. This macronutrient profile makes cheese sticks a relatively energy-dense snack, contributing significantly to daily caloric intake.
Cheese stick nutrition information is crucial for making informed snack choices! Want to compare protein and fat content? Check out the detailed breakdown of daisy cottage cheese nutrition for a fantastic alternative. Understanding both helps you balance your daily dairy intake and choose the perfect cheesy treat for your needs!
The high fat content primarily consists of saturated fat, a factor to consider for individuals monitoring their saturated fat intake.
Micronutrient Content of Cheese Sticks
Beyond macronutrients, cheese sticks are a source of several essential micronutrients. They are particularly rich in calcium, crucial for bone health, and phosphorus, which plays a vital role in energy metabolism and cell function. Cheese sticks also contain varying amounts of vitamins, including vitamin A, which supports vision and immune function, and vitamin B12, essential for nerve function and red blood cell formation.
The specific amounts of these vitamins and minerals will depend on the type of cheese and the manufacturing process. For example, cheddar cheese tends to be higher in vitamin A than mozzarella.
Nutritional Differences Between Cheese Stick Varieties
The nutritional content of cheese sticks varies significantly based on the type of cheese used. Cheddar cheese sticks, for instance, tend to be higher in fat and protein than mozzarella cheese sticks. Mozzarella, on the other hand, often contains slightly less fat and protein but may be higher in moisture content. String cheese, a popular variation, generally mirrors the nutritional profile of the cheese it is made from.
The processing methods also influence the final nutritional values; some manufacturers may add extra ingredients, affecting the overall composition.
Comparative Nutritional Information for Common Cheese Stick Varieties
| Nutrient | Cheddar Cheese Stick (28g) | Mozzarella Cheese Stick (28g) | String Cheese (28g) (Cheddar) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 110-130 | 90-110 | 110-130 |
| Protein (g) | 7-8 | 6-7 | 7-8 |
| Fat (g) | 9-10 | 7-8 | 9-10 |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 1-2 | 1-2 | 1-2 |
| Calcium (mg) | 200-250 | 180-220 | 200-250 |
| Vitamin A (mcg) | 150-200 | 50-100 | 150-200 |
| Vitamin B12 (mcg) | 0.5-1.0 | 0.5-1.0 | 0.5-1.0 |
Serving Size and Portion Control: Cheese Stick Nutrition Information
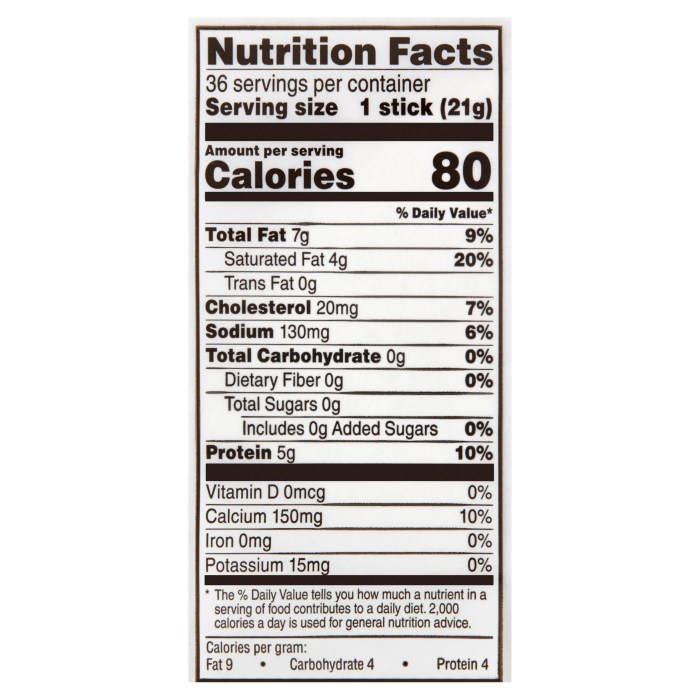
The seemingly innocuous cheese stick, a convenient and palatable snack, presents a subtle yet significant challenge to maintaining a healthy diet: portion control. Understanding appropriate serving sizes and employing effective strategies to manage consumption is crucial for preventing potential health consequences associated with overindulgence. This section will explore the importance of adhering to recommended serving sizes, provide practical tips for portion control, and detail the potential negative impacts of excessive cheese stick consumption.The recommended serving size of cheese sticks, like many processed foods, directly influences caloric intake and nutrient balance.
Consuming more than the recommended amount can lead to an excess of saturated fat, sodium, and calories, potentially contributing to weight gain, increased cholesterol levels, and other health problems. Conversely, adhering to recommended portion sizes allows for the enjoyment of cheese sticks as part of a balanced diet without compromising overall health goals.
Strategies for Portion Control
Effective portion control strategies are essential for managing cheese stick consumption. Pre-portioning cheese sticks into individual servings before storing them can significantly aid in limiting consumption. This simple act removes the temptation of reaching for multiple sticks without conscious consideration. Alternatively, pairing cheese sticks with a substantial amount of fruits, vegetables, or whole grains can create a more balanced snack and naturally reduce the overall consumption of cheese sticks.
Mindful eating, paying close attention to hunger and satiety cues, is another valuable tool. By slowing down and savoring each bite, individuals can better assess their fullness and prevent overeating.
Consequences of Excessive Consumption
Excessive consumption of cheese sticks can have several detrimental effects on weight management and overall health. The high fat and calorie content contributes to positive energy balance, leading to weight gain over time. Furthermore, the high sodium content can elevate blood pressure, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Regular consumption of excessive amounts of saturated fat, a prominent component of cheese sticks, can also contribute to elevated cholesterol levels, further increasing the risk of heart disease.
These potential consequences underscore the importance of mindful consumption and adherence to recommended serving sizes.
Appropriate Serving Sizes for Different Age Groups and Activity Levels, Cheese stick nutrition information
The following infographic illustrates appropriate serving sizes, acknowledging that individual needs vary based on age, activity level, and overall dietary requirements. It is important to note that these are general guidelines and individual needs should be determined in consultation with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.Infographic: A visual representation (descriptive text only) showing a chart with columns for Age Group (e.g., Children 2-5, Children 6-12, Teenagers 13-18, Adults 19+), Activity Level (Low, Moderate, High), and Recommended Serving Size (e.g., 1 stick, 1-2 sticks, 2 sticks, etc.).
The chart visually depicts that generally, older age groups and higher activity levels correlate with slightly larger serving sizes, always within the bounds of a balanced diet and overall health considerations. The chart explicitly mentions that these are guidelines and individual needs might differ. It also includes a note recommending consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized recommendations.
FAQ Summary
Are cheese sticks a good source of protein?
Yes, cheese sticks provide a moderate amount of protein, contributing to daily protein intake. However, the exact amount varies depending on the type and size of the cheese stick.
Are all cheese sticks created equal nutritionally?
No, the nutritional content of cheese sticks varies significantly depending on the type of cheese used (e.g., cheddar, mozzarella), the ingredients, and the processing methods. Always check the nutrition label.
Can people with lactose intolerance eat cheese sticks?
Many cheese sticks contain lactose, so individuals with lactose intolerance may experience digestive discomfort. Lactose-free cheese sticks are available, but it is crucial to check the ingredients list.
How many cheese sticks should I eat per day?
The recommended serving size varies depending on individual dietary needs and overall calorie intake. It is best to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice.
